Xenomics – Breaking Boundaries to Build a Future
As technology moves forward, its applications in the world of science also seem to exponentially improve, not only in the development of new approaches but in the increments in efficiency and effectiveness of existing ones. One clear example of this progress is seen in the field of genetics, since improvements in the handling of big data allows for faster and more precise procedures.
Xenomics rises as one of these projects, by presenting a new way to execute the CRISPR process for an increase in speed, accuracy and, consequently, applicability. In its current stage, this method of gene editing is limited by a high error rate and a slow rate of completion (approximately 8 weeks per experiment), only allowing for 50-60 base pair edits or inserts and a single strain per edit.
Lighting the Way
To paint a better picture: CRISPR Cas9 is a process in genetic engineering that inserts CRISPR, specialized sequences of DNA, into big strands by using the Cas9 protein, in a similar manner on how bacteria develop defenses against viruses and other foreign organisms.
By developing a new process for gene editing, Xenomics is able to achieve the same results as regular CRISPR Cas9 in only a fraction of the time, with 8 weeks being equivalent to 460 years of iterative CRISPR, as it allows for inserting genes of 8.000 base pairs at a time thanks to 160 quadrillion unique combinations of promoters and terminators.
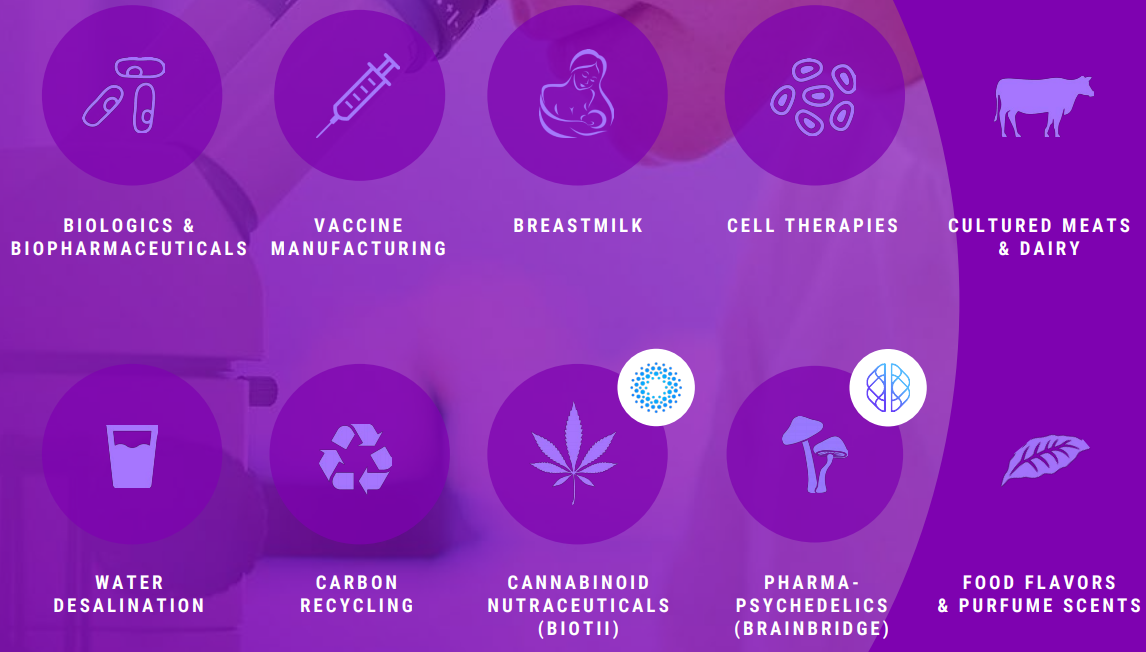
A faster, more efficient process will always be more attractive, not only within the scientific environment, but also to enthusiasts looking for applications. This is the reason why Xenomics is interested in lending their services for projects in very diverse fields: pharmaceutics, water desalination, carbon recycling, cultured meats and dairy, cell therapies, cannabinoid products and many others, given their capability for creating super-organisms that can be programmed to perform any function required in the situation.
Early Birds and Market Disruption
Due to their potential, Xenomics was promptly contacted by Biotii to use their service to bio-sinthesize cannabinoids. This deal meant Biotii had exclusive access to the process and represented $6 million linked to different terms, while Xenomics now owns 58% of Biotii.
This industry, controversial as it may be, is growing at a steady pace, with legislations all around the world becoming more permissive towards the use of these substances to treat symptoms of a variety of conditions. By using specialized organisms in the manufacturing process, the purity and effectiveness of these cannabinoid compounds can be drastically improved, while reducing productions costs and allowing for increased supply.
Once the deal with Biotii is finished, Xenomics will endeavor into new projects with the aim to actively participate in solving humanities major problems (pollution, vaccine development, tobacco related deaths, global hunger, shortage of fresh water, mental health, depletion of fossil fuels, etc.) making effective use of one of the greatest advancements in gene editing technology.